
The panel regression analysis is applied to the sample of 39 global cities over the period from 2013 until 2019 and the data on urban functions are obtained from the Global Power City Index (GPCI). Starting from that point of view, this paper aims to identify the main urban functions that influence the cities' size with an analysis focusing on global cities worldwide. Although financial wellbeing and incentives were considered to be a key factor of urban magnetism, contemporary research approaches have emphasized other factors that may influence urban attractiveness. The analysis of the determinants of urban magnetism can facilitate the formulation of concrete actions aimed at increasing the attractiveness of the city, which ultimately leads to the preservation of long-term socio-economic development of cities. In such conditions, city leaders face the need to understand the concept and factors of urban magnetism. Nonetheless, accelerated globalization has conditioned direct competition of global cities for different resources, and one of the most desirable being highly-skilled, talented and creative residents. In the hierarchy of global cities, those who successfully use the limited available resources and offer an adaptable and flexible living environment, represent the most competitive global cities.
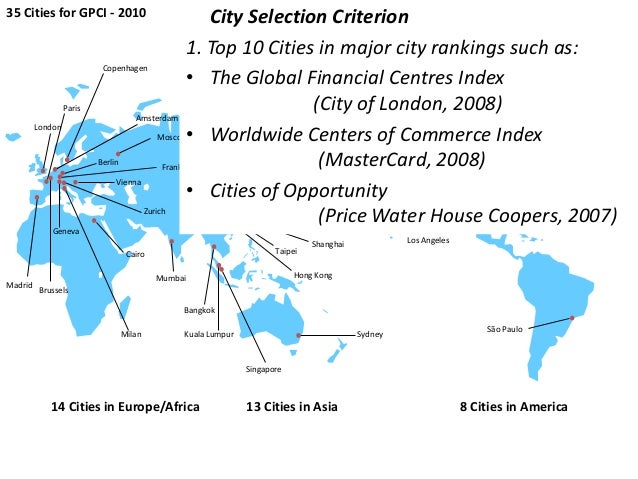
Abstract : Dynamics in global processes have led to a number of political, economic and cultural changes that have resulted in the emergence of global cities.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
